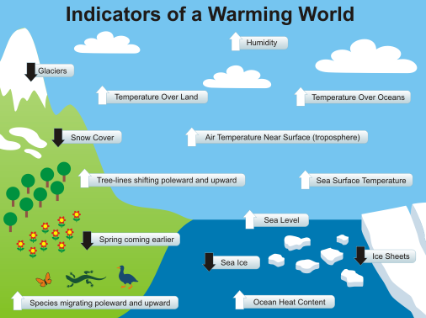
Introduction
In the scorching summer of 2024, India found itself grappling with one of the most severe heat waves in recent memory. As temperatures soared to unprecedented heights across the subcontinent, the impact on daily life, agriculture, and the environment was profound and far-reaching. Let’s delve into the details of this extraordinary weather event and its implications.
The Heatwave Unfolds
The heatwave struck early in the summer season, catching many by surprise. Cities accustomed to hot weather were suddenly facing temperatures several degrees above normal. Temperatures in the capital New Delhi alone exceeded nearly 53 °C (127 °F). It was considered the country’s hottest summer in 120 years.
Climate change, predominantly caused by burning fossil fuels and exacerbated by human interference, is making heatwaves hotter. This is more likely to happen all over the world, according to researchers. The heatwave in India was made 45 times more likely due to climate change. Also the recurrence of extreme heat incidents are likely as the global temperature goes up from the current 1.2 degrees Celsius towards 2 degrees Celsius, according to a study by the World Weather Attribution (WWA).
Dr Friederike Otto, Imperial College London and director of World Weather Attribution says,“This devastating heat is not a natural disaster. The suffering India is facing is worse because of climate change caused by burning coal, oil and gas and deforestation. What we are seeing in India is exactly what scientists said would happen if we didn’t stop heating the planet. To avoid making the problem worse, the world needs to end fossil fuel use. Unless we do it, terrible heat like this will happen more and more often, and it will get even hotter. The heat will become worse, and the death toll will continue to rise, fast.”
Heatwave: Human Toll and Public Health Crisis
The heatwave quickly escalated into a public health crisis. Hospitals overflowed with patients suffering from heat exhaustion, heatstroke, and dehydration. Vulnerable populations, including the elderly, young children, and those engaged in outdoor labor, were particularly at risk. Government agencies scrambled to set up cooling centers and distribute water to affected areas. Even then the sheer intensity of the heatwave strained resources to their limits.
According to Dr. Krishna AchutaRao, a renowned Professor and Dean at the Centre for Atmospheric Sciences(Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi) the prevailing heatwave conditions experienced not only in India but also in various parts of the world. Also these are a direct consequence of climate change resulting from human emissions of greenhouse gas. It is imperative that immediate measures be taken to mitigate the escalating global average temperatures; otherwise, the consequences are evident.
With temperatures surpassing 45ºC in at least 37 cities, there is a significant risk of heat-related illnesses for the entire population. Disturbingly, there have already been over 16,000 cases of heat stroke and 60 heat-related fatalities since March 2024. Although these figures are likely a substantial underestimation.
Impact on Agriculture and Economy
India’s agrarian economy felt the heatwave’s impact acutely. Crops withered under the relentless sun, leading to significant losses for farmers already grappling with erratic weather patterns. Water scarcity worsened as rivers and reservoirs dried up, exacerbating the agricultural crisis. The economic ripple effects were felt across sectors, from reduced productivity to increased prices for essential commodities.
This year, Asia has experienced an exceptionally hot summer. This phenomenon, that scientists explain is due to the exacerbation of human-induced climate change. In central India, Rajasthan has been particularly affected by scorching temperatures, reaching up to 50 degrees Celsius in certain districts. According to government data, there have been 4 fatalities since March, along with 451 cases of heat stroke reported.
Conversely, northeastern India has been facing heavy rainfall following cyclone Remal, resulting in numerous landslides. Additionally, parts of Assam, which shares a border with Bangladesh, are currently experiencing flooding.
Environmental Consequences
The environmental repercussions of the heatwave were dire. Wildlife habitats were threatened as natural water sources dried out, forcing animals to migrate in search of sustenance. Forest fires broke out in several regions, exacerbated by dry conditions and high temperatures. Air quality plummeted in urban areas as stagnant air trapped pollutants, posing additional health risks to residents.
Heatwave: Lessons Learned
The 2024 heatwave in India served as a stark reminder of the growing threat posed by climate change. It underscored the need for proactive measures to build resilience and adapt to extreme weather events. From investing in climate-resilient infrastructure to promoting sustainable agricultural practices, the heatwave prompted a reevaluation of priorities at every level of society.
Aarti Khosla, Director of Climate Trends, emphasizes the need for immediate changes to mitigate the heat island effect. The urban population in India has surged to 460 million between 1970 and 2018, leaving over one-third of Indians highly susceptible to climate risks, which adversely affect their well-being and productivity.
Ethanol: A bio-fuel to combat climate change
Renewable fuels like ethanol, which are available right now, have the capacity to lead the charge against fossil fuels and help decarbonize the economy by reducing greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions. Studies have shown that Grain-based ethanol cuts GHG emissions by 44 to 52% compared to gasoline while 2G ethanol made from biomass takes this one step further and cuts down on GHG emissions by a whopping 80%.
Ethanol has a proven track record of cutting GHG emissions from transportation. The use of ethanol in gasoline in 2023 in the USA reduced CO2 equivalent greenhouse gas emissions from transportation by 56.5 million metric tons. That’s equivalent to removing 12 million cars from the roads for a whole year. In addition to reducing GHG emissions, ethanol is the best tool available to reduce tailpipe emissions of other harmful pollutants like carbon monoxide, air toxins and fine particulate matter.
While Ethanol has gained popularity in India over the years, its adoption is still slow due to scarcity of raw material for producing ethanol from traditional sources including sugarcane juice, broken rice and other grains. 2G ethanol made from biomass residue is the answer to this problem. There is an abundance of biomass residue, most of which is currently being burnt in India (rice straw), which in fact leads to pollution and contributes significantly to climate change. Investing in 2G ethanol technology is the way forward, which will help India reach its net zero target by 2050 by significantly reducing GHG emissions and decarbonizing the economy. We at Khaitan Bio Energy are continuously working to help achieve this by providing end to end solutions for producing 2G ethanol using our patented technology.
Looking Ahead
As the temperatures gradually returned to normal, the scars left by the 2024 heatwave remained. The experience fueled discussions on climate policy, resilience-building, and the imperative of global cooperation in tackling climate change. While the immediate crisis subsided, its lessons echoed far beyond India’s borders, urging nations worldwide to prioritize climate action for a sustainable future.
In conclusion, the 2024 heatwave in India was a wake-up call—an urgent reminder of the need for concerted efforts to mitigate climate risks and protect vulnerable communities. It underscored the interconnectedness of environmental, social, and economic factors in shaping our response to climate change. As we reflect on this unprecedented event, the imperative to act decisively and collectively has never been clearer.