We are all acutely aware of the current state of climate change. Wind patterns, temperature, air pressure, and humidity influence our climate. Several climates worldwide include dry, mild, tropical, and more. The seasons there are determined by the temperature. Since we are living creatures, our environment impacts all aspects of our existence. To live a regular life, we thus need a steady and healthy one. However, this trend is being disturbed by global warming.
How does global warming work?
Procedures that cause the earth’s temperature to grow consistently and continuously. A grave issue will put all living things in serious peril. Likewise, there are several causes for this occurrence.
Increased carbon dioxide levels and greenhouse gases are significant contributors to it. Living things will soon meet their demise if we do not take action to solve this issue. Furthermore, we must be aware of its adverse effects to act quickly to remedy it.
Everyone must be made aware of their role in the rising global warming. To rescue the world and all of its inhabitants, it is crucial that we discover a solution that will enable us to address this problem as soon as possible.
Impact of global warming
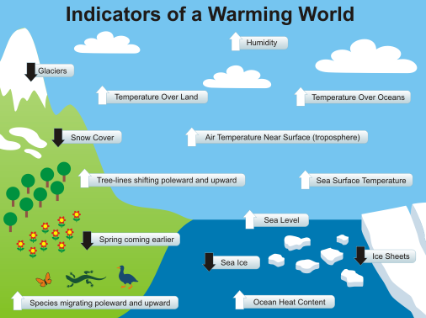
By now, we must all be aware that the earth’s temperature has risen by one degree Celsius. Even though it appears to be a modest number presently, the effects it causes are enormous. Increasing this temperature by even one degree Celsius requires significant energy, and our climate system would need to be force-fed with this additional energy.
A constant increase in the earth’s temperature is called global warming. The generation of greenhouse gases like carbon dioxide and methane is a significant factor in this increase. Several scientific arguments show that the earth’s temperature has risen, especially since the 1950s. The world’s climate system has warmed due to human activity during the past several decades, and it is expected that the global surface temperature will likely increase much more in the twenty-first century. This temperature increase is negatively impacting the earth’s life. Here is a thorough examination of the effects of global warming.
Effects on Climate
The precipitation pattern has changed due to global warming in several parts of the world. As a result, some areas are suffering flooding while others are experiencing draught-like conditions. In this manner, the moist parts become wetter while the dry ones get dryer. Along with other environmental changes, an increase in temperature is also causing storms, cyclones, heat waves, and wildfires. Global warming is causing extreme weather in many areas of the world, and the issue is only predicted to worsen.
Effects on Sea
Over the 20th century, the sea level has increased worldwide. This increase in sea level can be attributed to two main factors. Two things have happened: first, there was a thermal expansion brought on by the warming of the ocean, and second, there has been an increase in the melting of land-based ice. According to predictions, the sea level will increase significantly shortly. Living in coastal and low-lying areas is seriously threatened by rising sea levels.
Effects environment
Because of global warming, the earth’s entire environment has suffered. This temperature increase worsens air pollution by increasing ground level ozone, which is created when smoke from industries, automobiles, and other sources reacts with heat and sunshine to generate ozone. Increased air pollution has brought numerous health issues, and things are worsening every day.
Effects of Life on earth
Life on Earth has been severely harmed by the rise in temperature, unpredictable climatic conditions, and air and water pollution. Numerous lives have been lost due to regular floods, droughts, and cyclones, and the rising pollution levels contribute to several health issues.
Like humans, many other animals and plants cannot adapt to the shifting weather. They are suffering from the adverse effects of the quick changes in the land and water meteorological conditions. The number of animals and plants going extinct has increased. According to studies, the growing amount of pollution and climatic changes are to blame for the extinction of several species of birds, mammals, reptiles, fish, and amphibians.
Agriculture is Affected
The unpredictable rainfall pattern brought on by global warming has most severely impacted agriculture. While specific locations frequently experience draught-like conditions, others often see severe rain and flooding. This is harming the crops as well as the residents of those places. Crops are suffering, and agricultural fields are losing their fertility.
Sea Level Will Rise 1-8 feet by 2100
Since accurate records have been kept since 1880, the sea level has increased by around 8 inches (0.2 meters) worldwide. If carbon emissions continue at their current rate, by the year 2100, experts predict they will have risen by at least another foot (0.3 meters) and perhaps even by as much as 8 feet (2.4 meters). The expansion of seawater as it heats and the additional water from melting land ice are the two main causes of sea level rise.
Even small sea level changes can cause increased flooding because storm surges and high tides combine with sea level rise and land sinking along coastlines to amplify flooding in some regions. Sea level rise will continue past 2100 because the ocean takes a long time to respond to warmer conditions at Earth’s surface fully. As ocean waters continue to warm, sea levels will continue to rise.
Changes in the climate will persist throughout.
It is predicted that the global climate will continue to warm throughout this century and beyond. The quantity of heat-trapping gases generated by people and how susceptible the Earth’s climate is to those emissions determine the extent of climate change and the severity of repercussions.
Hurricanes Will Become Stronger and More Intense
The intensity of North Atlantic hurricanes and the frequency of the strongest hurricanes have increased since the early 1980s. Scientists project that hurricane-associated storm intensity and rainfall rates will increase as the climate continues to warm.
Longer Wildfire Season
Warming temperatures have made the wildfire season longer and more severe in the West, and deepening drought in the region has increased the risk of fires. Scientists estimate that human-caused climate change has already doubled the area of forest burned in recent decades. By around 2050, the amount of land consumed by wildfires in Western states is projected to increase by two to six times. Wildfires are projected to increase by about 30% in rainy regions like the Southeast.
Globally, fire weather seasons have lengthened. Drought remains the dominant driver of fire emissions, but recently there has been increased fire activity in some tropical and temperate regions due to warmer temperatures that increase vegetation flammability. The northern boreal zone (Earth’s northernmost forests) near the Arctic is also experiencing more prominent and frequent fires, which may increase under a warmer climate.
More fires and a more extended fire season are causing an additional health hazard of wildfire smoke, which affects tens of millions of people in the United States. Meanwhile, the costs of fighting wildfires have risen 11-fold over the past 30 years, adding a financial burden on top of the public health risk.
More heat waves and droughts
Heat waves (prolonged periods of exceptionally hot weather) and droughts in the Southwest are expected to intensify, making cold waves less severe and more common. The temperature is expected to rise throughout the year.
Modifications in Rainfall Patterns
The United States has unequal effects of climate change on precipitation (rain and snow), with some areas experiencing greater rainfall and floods while others are facing drought. Scientists predict that the northern United States will get more winter and spring precipitation this century than the Southwest.
Future climate projections over the U.S. suggest the recent trend toward increased heavy precipitation events will continue. This means that while it may rain less frequently in some regions (such as the Southwest) when it does rain, heavy downpours will be more common.
The growing season (and the frost-free season) will extend.
Since the 1980s, the length of the frost-free season and the accompanying growing season have increased, with the western United States experiencing the largest increases. The lengthening of the growing season will continue across the country, impacting ecosystems and agriculture.
The length of the growing season is predicted to expand by a month or more throughout the majority of the United States by the end of the century if heat-trapping gas emissions continue to increase at the current rates, with slightly lower increases in the northern Great Plains. The frost-free season might last eight weeks in the western United States, particularly in high-elevation and coastal regions. If we decrease our emissions of gases that trap heat, the rises will be noticeably less.
Arctic Is Very Likely to Become Ice-Free
Sea ice cover in the Arctic Ocean is expected to continue decreasing. The Arctic Ocean will likely become ice-free in late summer if current projections hold; this change will likely occur before mid-century.
Conclusion
The issue of global warming is quite severe and has disastrous consequences. Immediate action must be taken to reduce carbon emissions to mitigate the effects of global warming. This is feasible if every person puts forth a little effort for the cause.

