Introduction
As climate concerns become more urgent and fossil fuel supplies increasingly uncertain, 2025 marks a critical turning point for the transportation sector. In this green transition, three sustainable alternatives—biofuels, electric vehicles (EVs), and green hydrogen—are leading the way toward cleaner, more efficient mobility. Together, they promise to reduce carbon emissions, support energy independence, and reshape how people and goods move across cities, countries, and continents.
This blog explores how these three technologies are shaping India’s and the world’s mobility landscape in 2025, the challenges they face, and the crucial role of policy, innovation, and industry players like Khaitan Bio Energy in driving change.
Why Green Mobility Matters Now More Than Ever
Transportation accounts for nearly 25% of global CO₂ emissions, with road transport being the biggest contributor. In India, the sector is not just a source of pollution but also a major drain on imported fossil fuels. As cities choke on smog and fuel prices fluctuate, governments, businesses, and citizens are realizing the need to transition to greener options.
Key Goals of Green Mobility:
- Reduce dependence on imported oil
- Cut greenhouse gas and particulate emissions
- Improve urban air quality
- Create local jobs in clean tech sectors
- Align with international climate targets (like Net Zero by 2070 for India)
Green Mobility – A Bridge Toward Cleaner Transport
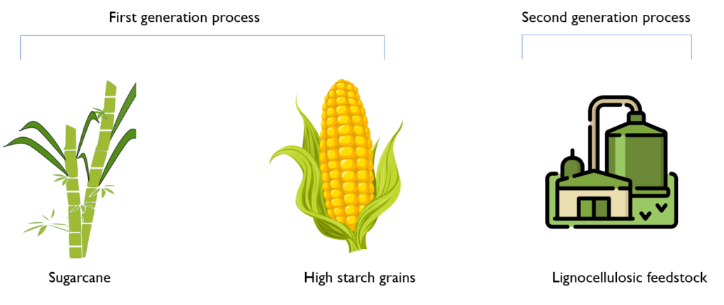
Biofuels, particularly ethanol and biodiesel, are renewable fuels made from organic materials like sugarcane, maize, used cooking oil, and agricultural waste. In India, the Ethanol Blending Programme (EBP) aims to blend 20% ethanol into petrol by 2025–26.
Benefits of Biofuels:
- Can be used in existing internal combustion engine vehicles (ICEVs)
- Lower lifecycle emissions compared to petrol and diesel
- Stimulate rural economy by utilizing agricultural waste
- Reduce stubble burning by using crop residues like rice straw
Types of Biofuels:
| Type | Source | Use Case |
| 1G Ethanol | Sugarcane, corn | Petrol blending |
| 2G Ethanol | Rice straw, agri waste | Cleaner, non-food-based fuel |
| Biodiesel | Used cooking oil, animal fats | Diesel vehicle alternative |
| Bio-CNG | Organic municipal/agri waste | Public transport, logistics |
Real-world Impact:
By February 2025, India has reached nearly 17.98% ethanol blending, and new 2G ethanol plants are being commissioned across the country.
Khaitan Bio Energy
Khaitan Bio Energy is among the pioneers producing 2G ethanol from rice straw, using zero-liquid discharge (ZLD) technology and valorizing byproducts like silica and lignin. Their work directly contributes to reducing stubble burning and achieving India’s blending goals—while empowering farmers with new income streams.
Electric Vehicles (EVs) – Quiet, Efficient, and Rapidly Scaling
EVs have gained tremendous momentum globally and in India. With government subsidies, improved infrastructure, and rising consumer interest, EVs are transitioning from niche to mainstream.
Advantages of EVs:
- Zero tailpipe emissions
- Lower maintenance and running costs
- Growing charging infrastructure
- Quiet and smooth driving experience
Challenges:
- High upfront cost (though decreasing)
- Battery range anxiety
- Charging station availability in rural areas
- Recycling and sourcing of rare earth minerals
Government Support in 2025:
- FAME II Scheme continues to offer incentives for two-, three-, and four-wheelers.
- State governments offer tax exemptions, registration fee waivers, and subsidies.
- Many cities are shifting public buses and taxis to electric fleets.
Trends in 2025:
- Electric two-wheelers and rickshaws dominate the urban mobility space.
- Battery-as-a-service and swapping models are expanding in metro areas.
- Companies like Tata Motors, Ola Electric, Ather, and MG have launched newer, more affordable EV models.
Hydrogen – The Future Fuel?
Hydrogen, especially green hydrogen produced using renewable electricity, is gaining interest for hard-to-decarbonize sectors like heavy-duty transport, shipping, and aviation.
Why Hydrogen?
- High energy density and long driving range
- Can fuel large vehicles like buses, trucks, and trains
- Emission-free when used in fuel cells (only water as a byproduct)
India’s Hydrogen Push:
In 2023, the government launched the National Green Hydrogen Mission, aiming to make India a global hub for hydrogen production and exports. By 2025:
- Pilot projects are running hydrogen buses in cities like Delhi and Pune.
- Green hydrogen is being used in some industrial and rail transport applications.
- Investments are flowing into electrolyzer manufacturing and hydrogen infrastructure.
Challenges Ahead:
- High production and storage cost
- Lack of fueling infrastructure
- Competition with other clean energy sources
Comparing the Three Pillars of Green Mobility
| Feature | Biofuels | EVs | Hydrogen |
| Fuel Source | Organic materials/agri waste | Electricity (ideally renewable) | Electrolyzed water (green) |
| Emissions | Low lifecycle emissions | Zero tailpipe | Zero tailpipe |
| Infrastructure | Existing ICE vehicles usable | Requires charging network | Needs hydrogen refueling |
| Scalability in 2025 | High (with support) | Growing fast in cities | Early-stage (pilots ongoing) |
| Ideal For | Rural mobility, farming, logistics, Daily road transportation | Urban transport, personal use | Heavy vehicles, rail, industry |
The Role of Policy and Innovation
The future of green mobility doesn’t rely on a single solution. A multi-tech approach is key—using the best fuel or vehicle type for the right application.
Governments must continue to:
- Provide incentives for clean vehicle adoption
- Invest in renewable energy and infrastructure
- Encourage R&D in storage, fuel cells, and recycling
- Support startups and biofuel plants like Khaitan Bio Energy
Private sector innovation, from battery management to biomass processing, is also essential. Collaboration between EV makers, fuel producers, and smart grid developers can accelerate the transition.
What Can Individuals and Businesses Do?
For Individuals:
- Choose an EV or FFV (flex-fuel vehicle) for your next purchase.
- Support brands that prioritize sustainability.
- Spread awareness and demand clean transport options.
For Businesses:
- Electrify your vehicle fleet where feasible.
- Partner with 2G biofuel producers for low-emission logistics.
- Use renewable energy in warehousing and transport hubs.
Conclusion: A United Path Toward Cleaner Roads
The transportation sector is undergoing a massive transformation in 2025. While electric vehicles are capturing urban markets and green hydrogen is shaping up for the long haul, biofuels like those produced by Khaitan Bio Energy are proving essential for bridging the gap—especially in agriculture and rural India.
Each solution has a unique role to play. Together, they form the foundation of green mobility—a path that ensures cleaner air, economic growth, and energy security for the generations to come.
India’s green future is not a dream—it’s in motion. The road ahead is electric, bio-powered, and hydrogen-fueled.