Introduction
India’s clean energy vision is transforming rapidly, powered by breakthroughs in biofuel. The journey from first-generation to third-generation ethanol marks an evolution in how the country can address energy needs, pollution, and food security. The question, “Can 3G Ethanol Outperform 2G?” is especially relevant as companies like Khaitan Bio Energy (KBIO) set the pace with innovative solutions.
Understanding the Generations: 2G vs 3G Ethanol
What is 2G Ethanol?
2G ethanol is produced by converting non-food agricultural residues (like rice straw, corn stover, and bagasse) into biofuel with advanced technologies. This sidesteps the food-versus-fuel debate and utilizes waste that would otherwise be burned, causing massive pollution.
- Feedstock: Non-food cellulose (rice straw, wheat straw, corn stover)
- Process: Cellulosic fermentation, enzymatic breakdown of cellulose
- Environmental Impact: Reduces stubble burning, lowers greenhouse gases
- Commercial Example: Khaitan Bio Energy’s patented technology, validated in partnership with BIRAC and through pilot plants since 2021
What is 3G Ethanol?
3G ethanol represents the cutting edge: biofuel derived from algae or other advanced microorganisms, grown in bioreactors. These sources don’t require arable land and use wastewater, sunlight, and CO₂.
- Feedstock: Algae, advanced microbes
- Process: Bio-reactors, innovative bioprocessing technology
- Environmental Impact: Wastewater recycling, maximized carbon capture, no land competition
- Deployment: Still at pilot stage; limited commercial scale; high costs
Comparative Analysis
Sustainability
| Attribute | 2G Ethanol | 3G Ethanol |
| Feedstock | Agricultural residue | Algae/microbes |
| Land use | Utilizes agricultural waste | No agricultural land needed |
| Food impact | Does not compete with crops | Completely decoupled from food |
| Water usage | Utilizes crop residue | May use wastewater, but scales are limited currently |
| GHG reduction | Significant | Potentially greater |
3G ethanol wins in sustainability—it is even more decoupled from food and land challenges than 2G, and has the potential for massive scale with enough investment.
Commercial Viability and Cost
| Attribute | 2G Ethanol | 3G Ethanol |
| Tech maturity | Commercial and pilot scale | Limited to pilot/research |
| Capital cost | Lower, proven | Higher, emerging |
| Production cost | Reasonable, declining with scale | Still high, needs breakthroughs |
| Deployment | Practically expanding (India/World) | Experimental, years out from scale |
Khaitan Bio Energy demonstrates that 2G ethanol is economically viable now, with a pilot plant and multiple proposed commercial facilities in Punjab and Uttar Pradesh. In contrast, 3G ethanol has not yet reached commercialization due to cost and complexity.
Market Impact: India’s Perspective
India set aggressive blending goals: 20% ethanol in petrol by 2025, with an increasing push towards advanced ethanol for future sustainability. The shock of declining sugar production in 2025 highlights why 2G technologies—like those led by Khaitan Bio Energy—are so critical to meeting mandates without threatening food security.
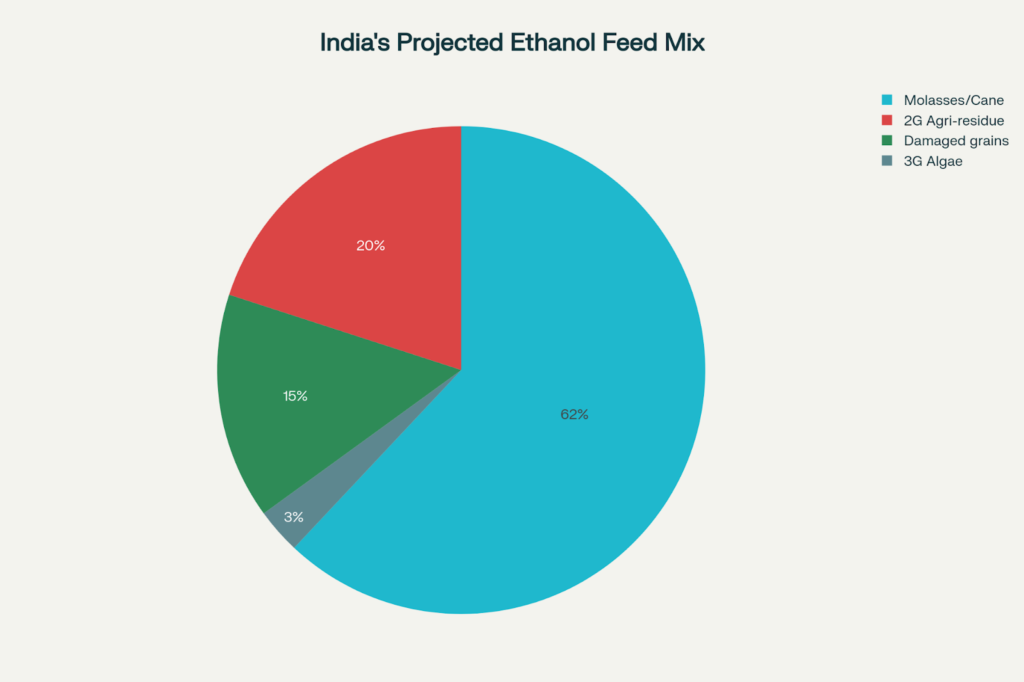
Pie Chart: India’s Ethanol Feedstock Mix (2026 and beyond, Projected)
Khaitan Bio Energy: Leading India’s 2G Ethanol Revolution
Khaitan Bio Energy illustrates what a technology-driven company can achieve—solving pressing environmental problems, delivering clean energy, innovating for economic value.
Innovations and Impact
- Zero-liquid discharge technology: Ensures no pollution from their ethanol plants, an edge over many competitors.
- Circular economy: Agricultural residue is purchased from farmers, incentivizing proper waste management and boosting rural income.
- Byproducts: Production of gypsum and precipitated silica from rice straw create additional value streams, lowering the net cost of ethanol.
- Scalable projects: Multiple 100 KLPD plants proposed in Punjab and Uttar Pradesh, using patented in-house technology that avoids conventional saccharification/fermentation limitations.
Government Alignment
India’s government supports advanced ethanol with subsidies, production incentives, and a commitment to net zero by 2050.
- Khaitan Bio Energy’s model has received strong support from PM JI-VAN Yojana, which backs projects using non-food biomass.
- Clarity on 2G pricing is being pushed, enabling technologies to scale faster.
The Road to 3G: Barriers and Potential
3G ethanol, while promising, faces considerable technical, economic, and industrial barriers:
- Scale: Current bioreactors/microalgal systems produce limited volumes.
- Cost: High due to equipment, expertise, and operational complexity—unit cost far above 2G ethanol.
- Technology: Needs breakthroughs in productivity, harvesting, and downstream processing.
- Indian Context: Most Indian ethanol expansion is 2G; 3G pilot projects exist but are years away from significant market impact.
Industry experts note that 3G could leapfrog 2G only with major R&D investment and widespread adoption of new techniques.
The Sustainability Edge
Both 2G and 3G are far superior to traditional fuels, but 2G is today’s solution, not just tomorrow’s hope. Khaitan Bio Energy’s approach minimizes environmental hazards and matches government goals for rural development, food security, and climate action.
Table: Sustainability Comparison
| Factor | 2G Ethanol (KBIO) | 3G Ethanol |
| CO₂ reduction | High | Highest (potential) |
| Land usage | No food competition | No land needed |
| Farmer income | Direct benefit | Minimal impact |
| Industrial maturity | Commercial-ready | Pilot/research |
| Waste valorization | Excellent | High, needs scale |
Conclusion: Why Khaitan Bio Energy Leads Today—and Prepares India for Tomorrow
- Today, 2G ethanol is the cornerstone of India’s clean energy transition, thanks to pioneering work by Khaitan Bio Energy, government policy, and urgent need to reduce pollution and food-versus-fuel tension.
- Tomorrow, 3G ethanol may become the gold standard for ultimate sustainability, using innovations from algae and other sources, but structural and economic barriers must be overcome first.
- Khaitan Bio Energy’s strategy—grounded in patented tech, circular economy, scalable projects, and government alignment—makes it the leading force for 2G ethanol now and a bridge for future breakthroughs.
India’s biofuel future will blend the best of 2G and 3G advances, with Khaitan Bio Energy showing how local innovation can deliver national progress—a model for the world.

